Perovskite
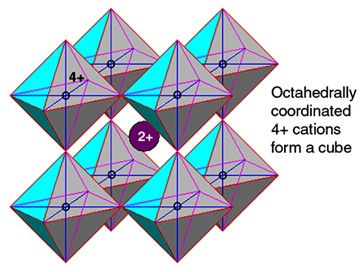
Term applied to A2+B4+O3 high-pressure minerals with a perovskite structure (general formula ABX3) where “A” is a metalElement that readily forms cations and has metallic bonds; sometimes said to be similar to a cation in a cloud of electrons. The metals are one of the three groups of elements as distinguished by their ionization and bonding properties, along with the metalloids and nonmetals. A diagonal line drawn that forms large cations such as Mg, Fe or Ca, “B” is another metal that forms smaller cations such as Si (called silicateThe most abundant group of minerals in Earth's crust, the structure of silicates are dominated by the silica tetrahedron, SiO44-, with metal ions occurring between tetrahedra). The mesodesmic bonds of the silicon tetrahedron allow extensive polymerization and silicates are classified according to the amount of linking that occurs between the perovskite), Ti and to a lesser degree Al, and “X” is typically oxygenElement that makes up 20.95 vol. % of the Earth's atmosphere at ground level, 89 wt. % of seawater and 46.6 wt. % (94 vol. %) of Earth's crust. It appears to be the third most abundant element in the universe (after H and He), but has an abundance only. Each B4+ ionAtom with a net electrical charge because it has lost, or gained, one or more electrons relative to the number possessed by a neutral atom of the same element. A positively charged ion (cation) has fewer electrons than a neutral atom; a negatively charged ion (anion) has more. is octahedrally coordinated with six oxygen atoms, and the A2+ ion sits in the center. Although ideally a cubic structure, the actual mineralInorganic substance that is (1) naturally occurring (but does not have a biologic or man-made origin) and formed by physical (not biological) forces with a (2) defined chemical composition of limited variation, has a (3) distinctive set of of physical properties including being a solid, and has a (4) homogeneous is slightly monoclinic because one unit cellSmallest repeating unit of a crystalline solid that can be used to describe the entire structure. Unit cells are like templates which can be copied to produce an entire crystal. angle is 90.67º. The magnesian end-member of silicate perovskite (MgSiO3 perovskite) is the most abundant mineral in the Earth’s lower mantleMain silicate-rich zone within a planet between the crust and metallic core. The mantle accounts for 82% of Earth's volume and is composed of silicate minerals rich in Mg. The temperature of the mantle can be as high as 3,700 °C. Heat generated in the core causes convection currents in (and thus inaccessible for study). Only after 50+ years of searching was this important high-pressure polymorph of enstatiteA mineral that is composed of Mg-rich pyroxene, MgSiO3. It is the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series - enstatite (MgSiO3) to ferrosilite (FeSiO3). (MgSiO3) finally discovered and identified in nature within the shocked Tenham meteoriteWork in progress. A solid natural object reaching a planet’s surface from interplanetary space. Solid portion of a meteoroid that survives its fall to Earth, or some other body. Meteorites are classified as stony meteorites, iron meteorites, and stony-iron meteorites. These groups are further divided according to their mineralogy and (as reported in 2014) and after characterization given the name bridgmanite. Interestingly, ringwoodite, the high-pressure olivineGroup of silicate minerals, (Mg,Fe)2SiO4, with the compositional endpoints of forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and fayalite (Fe2SiO4). Olivine is commonly found in all chondrites within both the matrix and chondrules, achondrites including most primitive achondrites and some evolved achondrites, in pallasites as large yellow-green crystals (brown when terrestrialized), in the silicate portion polymorph was also discovered in the Tenham meteorite in 1969. CaTiO3 perovskite is abundant within Calcium Aluminum-rich InclusionsSub-millimeter to centimeter-sized amorphous objects found typically in carbonaceous chondrites and ranging in color from white to greyish white and even light pink. CAIs have occasionally been found in ordinary chondrites, such as the L3.00 chondrite, NWA 8276 (Sara Russell, 2016). CAIs are also known as refractory inclusions since they (CAISub-millimeter to centimeter-sized amorphous objects found typically in carbonaceous chondrites and ranging in color from white to greyish white and even light pink. CAIs have occasionally been found in ordinary chondrites, such as the L3.00 chondrite, NWA 8276 (Sara Russell, 2016). CAIs are also known as refractory inclusions since they) and the Wark-Lovering rims (WLR) that surround many CAIsSub-millimeter to centimeter-sized amorphous objects found typically in carbonaceous chondrites and ranging in color from white to greyish white and even light pink. CAIs have occasionally been found in ordinary chondrites, such as the L3.00 chondrite, NWA 8276 (Sara Russell, 2016). CAIs are also known as refractory inclusions since they1.
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






