Opposition
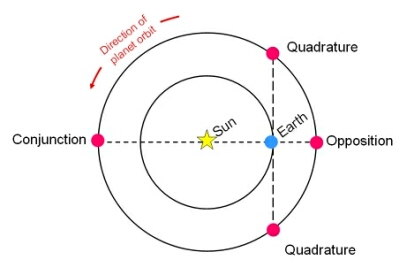
An object is at opposition when it is on the opposite side of the Earth from the SunOur parent star. The structure of Sun's interior is the result of the hydrostatic equilibrium between gravity and the pressure of the gas. The interior consists of three shells: the core, radiative region, and convective region. Image source: http://eclipse99.nasa.gov/pages/SunActiv.html. The core is the hot, dense central region in which the. The elongation of a Solar SystemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. body at opposition is 180°. The inferior planets, and other objects with orbits closer to the Sun than the Earth, can never be at opposition. Searches for new faint Solar SystemDefinable part of the universe that can be open, closed, or isolated. An open system exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings. A closed system can only exchange energy with its surroundings; it has walls through which heat can pass. An isolated system cannot exchange energy or matter with objects, such as Kuiper Belt ObjectsGenerally, small bodies found in the Kuiper Belt. The largest Kuiper Belt Object (KBO), Eris, is <3000 km in diameter. Image source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:EightTNOs.png Click on Term to Read More and asteroids, often attempt to findMeteorite not seen to fall, but recovered at some later date. For example, many finds from Antarctica fell 10,000 to 700,000 years ago. Click on Term to Read More these objects at opposition when they will have their maximum illumination by the Sun (i.e. their phase, if discernable, will be full).
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






