Nitrogen
Principal constituent of the Earth’s atmosphere (78.08 vol. % at ground level). Nitrogen is the fifth most abundant elementSubstance composed of atoms, each of which has the same atomic number (Z) and chemical properties. The chemical properties of an element are determined by the arrangement of the electrons in the various shells (specified by their quantum number) that surround the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of in the universeThat which contains and subsumes all the laws of nature, and everything subject to those laws; the sum of all that exists physically, including matter, energy, physical laws, space, and time. Also, a cosmological model of the universe. by atom abundance. Nitrogen comprises only 3.5 vol. % of the atmosphere of Venus and 2.7 vol. % of Mars’s atmosphere. Nitrogen has two isotopes: 14N (99.632 %) and 15N (0.368 %). Nitrogen isotopic variations are reported as δ15N in parts per thousand (‰) deviations from the nitrogen isotopic composition of Earth’s atmosphere (15N/14N = 0.003676).
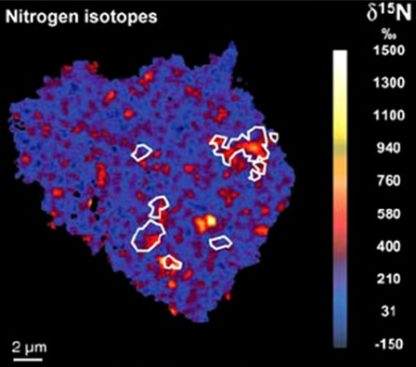
Large N isotopic variations are observed in the solar systemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. from -250 ‰ (lowest values in lunar soils) to 1600 ‰ (bencubinites). Comets Hale-Bopp and LINEAR have essentially identical δ15N values of ~940 ‰. Values of δ15N in the lunar regolithMixture of unconsolidated rocky fragments, soil, dust and other fine granular particles blanketing the surface of a body lacking an atmosphere. Regolith is the product of "gardening" by repeated meteorite impacts, and thermal processes (such as repeated heating and cooling cycles). show a very large range from ~100 ‰ to -250 ‰ with ratios appearing to vary with age. The lunar results can be explained by secular variation in δ15N of the solar windSupersonic flow of high-speed charged particles continuously blowing off a star (mostly e- and p+). When originating from stars other than the Sun, it is sometimes called a "stellar" wind. The solar wind may be viewed as an extension of the corona into interplanetary space. The solar wind emanates radially over time, although this hypothesis conflicts with the apparent stability of ratios in other solar wind volatile elementsChemical elements that condense (or volatilize) at relatively low temperatures. The opposite of volatile is refractory. Volatile elements can be divided into moderately volatile (Tc = 1230–640 K) and highly volatile (Tc < 640 K). The moderately volatile lithophile elements are: Mn, P, Na, B ,Rb, K, F, Zn. The moderately. Alternatively, the variation could result from mixing in a non-solar wind component (meteoriteWork in progress. A solid natural object reaching a planet’s surface from interplanetary space. Solid portion of a meteoroid that survives its fall to Earth, or some other body. Meteorites are classified as stony meteorites, iron meteorites, and stony-iron meteorites. These groups are further divided according to their mineralogy and or cometConglomeration of frozen water and gases (methane, ammonia, CO2) and silicates that that formed in the outer solar system and orbits the Sun. In recent years, the description of comets has shifted from dirty snowballs to snowy dirtballs with more dust than ice. However, the ratio is less than 10-to-1. material deposited on the moon during impacts). Extreme δ15N variations have been documented in organicPertaining to C-containing compounds. Organic compounds can be formed by both biological and non-biological (abiotic) processes. material from meteorites (image of insoluble organic matter extracted from the CR chondriteClass named for the Renazzo meteorite that fell in Italy in 1824, are similar to CMs in that they contain hydrous silicates, traces of water, and magnetite. The main difference is that CRs contain Ni-Fe metal and Fe sulfide that occurs in the black matrix and in the large chondrules EET 92042).
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






