Variable Star
StarSelf-luminous object held together by its own self-gravity. Often refers to those objects which generate energy from nuclear reactions occurring at their cores, but may also be applied to stellar remnants such as neutron stars. whose luminosityBasic property used to characterize stars, luminosity is defined as the total energy radiated by a star each second. An object’s luminosity is often compared to that of the Sun (Lsun = 4 × 1033 ergs/s = 3.9 × 1026 Watts). Luminosity has the same units as power (energy per Click on Term to Read More varies over time. Broadly speaking, variable stars are of two types: (1) stars that are intrinsically variable, that is, their luminosity actually changes, for example because the star periodically swells and shrinks; (2) eclipsing and rotating variables, where the apparent changes in brightness are a perspective effect. The first 334 variable stars discovered in a constellation are given a one or two letter code such as R Scuti or UV Ceti. Other variable stars are designated V335, V336, etc. For example, Proxima Centauri is known to variable star astronomers as V645 Centauri.
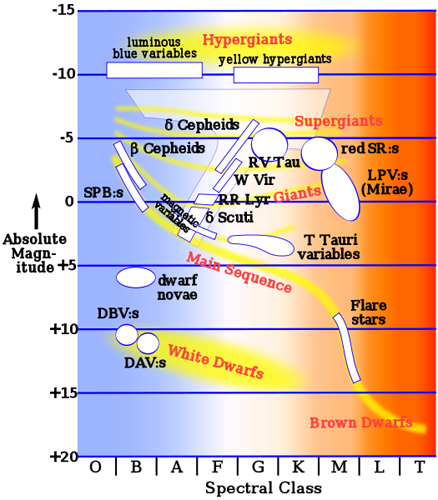
Image source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HR-vartype.svg.






