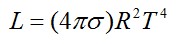Stefan-boltzmann Law
Law of blackbodyIdeal object that is a perfect absorber of light and also a perfect emitter of light. A perfect black body will absorb all radiation that falls on it, and will emit radiation that has a continuous spectrum determined only by the temperature of the black body: Where, T is the Click on Term to Read More radiation that states that the amount of energy given off by a blackbody per second per unit area (flux) is proportional to the fourth power of the temperature of the blackbody. For flux (power per area)
expressed as J/m2s with σ = 5.6703 x 10-8 W/m2K4:

If R is the radius of a starSelf-luminous object held together by its own self-gravity. Often refers to those objects which generate energy from nuclear reactions occurring at their cores, but may also be applied to stellar remnants such as neutron stars., its luminosityBasic property used to characterize stars, luminosity is defined as the total energy radiated by a star each second. An object’s luminosity is often compared to that of the Sun (Lsun = 4 × 1033 ergs/s = 3.9 × 1026 Watts). Luminosity has the same units as power (energy per Click on Term to Read More is: