Starburst Galaxy
Galaxies observed to be forming stars at an unusually fast rate (about 103 times greater than in a normal galaxyConcentration of 106 to 1012 stars, dust and gas, that are gravitationally bound. Our galaxy contains ~2 × 1011 stars. There are four main types of galaxies: • Elliptical
• Lenticular
• Spiral
• Irregular
Click on Term to Read More). At such high levels of starSelf-luminous object held together by its own self-gravity. Often refers to those objects which generate energy from nuclear reactions occurring at their cores, but may also be applied to stellar remnants such as neutron stars. formation, the supply of gas and dust within the galaxy would be exhausted within about 108 years. This indicates that these episodes of intense star formation started relatively recently and perforce will end relatively soon.
The areas of high formation rates may be spread throughout a galaxy, but most starbursts are observed in a small region around the nucleusCore of an atom, where nearly the entire mass and all positive charge is concentrated. It consists of protons and neutrons. Click on Term to Read More. Star formation is probably triggered by tidal interactions during galactic encounters, galactic mergers, or due to the presence of a galactic barUnit of pressure equal to 100 kPa., all of which result in the accumulation of substantial amounts of gas and dust in the central regions of the galaxy. Massive stars form from the available enshrouding gas and dust, which emit large amounts of UV radiation. This radiation is absorbed by the surrounding dust and reemitted at IR wavelengths, making starburst galaxies among the most luminous IR objects in the UniverseThat which contains and subsumes all the laws of nature, and everything subject to those laws; the sum of all that exists physically, including matter, energy, physical laws, space, and time. Also, a cosmological model of the universe.. SupernovaStellar explosion that expels much or all of the stellar material with great force, driving a blast wave into the surrounding space, and leaving a supernova remnant. Supernovae are classified based on the presence or absence of features in their optical spectra taken near maximum light. They were first categorized Click on Term to Read More explosions and stellar winds from the massive stars eventually sweep the gas from the galaxy and halt further star formation. Starburst galaxies appear to be more prevalent in the early universe than they are now. These galaxies, ~12 billion light years distant, appear to have characteristics similar to nearby starbursts and indicate that galaxy interactions were much more common in the past.
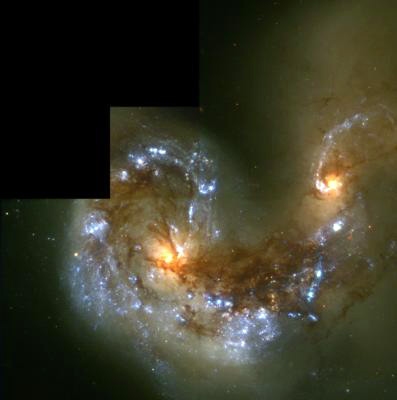
Image source: http://hubblesite.org/gallery/album/entire/pr1997034d/web/.






