Shield Volcano
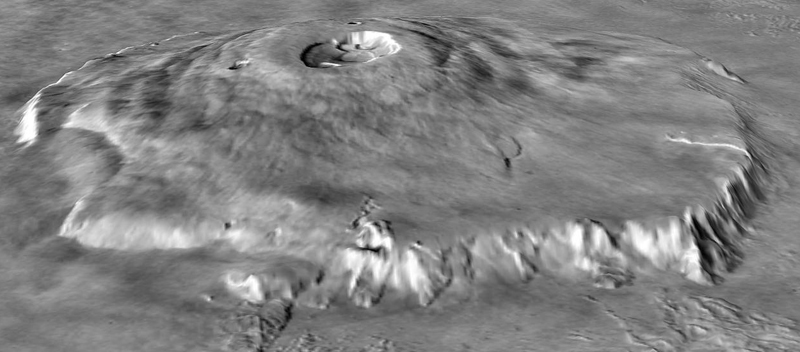
VolcanicIgneous rock that forms from cooling magma on the surface of a planet or asteroid. construction of a central type formed by repeated effusion of fluid (usually basaltic) lavaHot molten or semifluid rock derived from a volcano or surface fissure from a differentiated and magmatically active parent body.. The shield is characterized by a shallow flank, the steepness of which can vary from ~1° to 8°, however typical values are closer to ~5°. There often are one or more calderaLarge (>1 km) approximately circular volcanic depression, which may form by explosion or collapse, or a combination of the two. craters near the summit, like broad saucer-shaped cavities with steep walls. One of the largest shield volcanoes in the solar systemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. is Olympus Mons on Mars, with a diameter 624 km and height 25 km. It covers nearly the same area as the state of Arizona. The largest shield volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa on the Big Island of Hawaii with a diameter of 120 km and height of 10 km. An excellent explanation of why volcanoes are larger on Mars can be found at mars.nasa.gov.
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






