Peak Ring
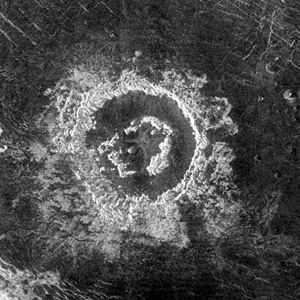
Central uplift characterized by a ring of peaks rather than a single peak. Peak rings are typical of larger terrestrial craters above ~50 km in diameter.
Barton CraterBowl-like depression ("crater" means "cup" in Latin) on the surface of a planet, moon, or asteroid. Craters range in size from a few centimeters to over 1,000 km across, and are mostly caused by impact or by volcanic activity, though some are due to cryovolcanism. on Venus. This 54-km (32-mi) diameter crater is the size at which craters on Venus begin to possess peak-rings instead of a single central peakExposed core of uplifted rocks in center of a complex impact crater. Central peak material typically shows evidence of intense fracturing, faulting, and shock metamorphism.. The floor of the crater is flat and radar-dark, indicating possible infilling by lavaHot molten or semifluid rock derived from a volcano or surface fissure from a differentiated and magmatically active parent body. flows sometime following the impact. Barton’s central peak-ring is discontinuous and appears to have been disrupted or separated during or following the cratering process.
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






