Long-Lived Radionuclides
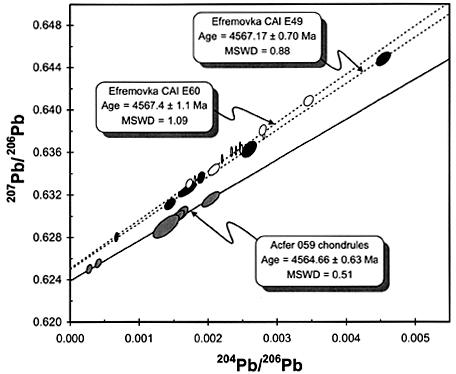
Radioactive isotopes with half lives (t½) exceeding ~500 Ma. They include: 238U (t½ = 4.47 Ga), 232Th (t½ = 14 Ga), 235U (t½ = 0.704 Ga), 40K (t½ = 1.25 Ga), and 87Rb (t½ = 48.8 Ga) and 147Sm (t½ = 106 Ga). Measuring the amount of the parent nuclideA nuclear species characterized by Z protons and N neutrons. Click on Term to Read More and the amount of the daughter isotopeOne of two or more atoms with the same atomic number (Z), but different mass (A). For example, hydrogen has three isotopes: 1H, 2H (deuterium), and 3H (tritium). Different isotopes of a given element have different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. Click on Term to Read More, and knowing the decay rate, allows calculation of the time since the daughter isotope began to accumulate. Long-lived radionuclides have reveled the absolute age of the solar systemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. (4.567 Ga) and the timing of major events on the Earth, Moon, and Mars. However, for the parent radionuclideRadioactive isotope - Atomic nuclide that decays radioactively . Click on Term to Read More to still be around to measure, it must decay very slowly. This means that the chronometers based on long-lived radionuclides inherently have low precision. The Pb-Pb systemDefinable part of the universe that can be open, closed, or isolated. An open system exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings. A closed system can only exchange energy with its surroundings; it has walls through which heat can pass. An isolated system cannot exchange energy or matter with, based upon decay of U and Th, provides the most precise dates of early solar system events.






