Cryovolcanism
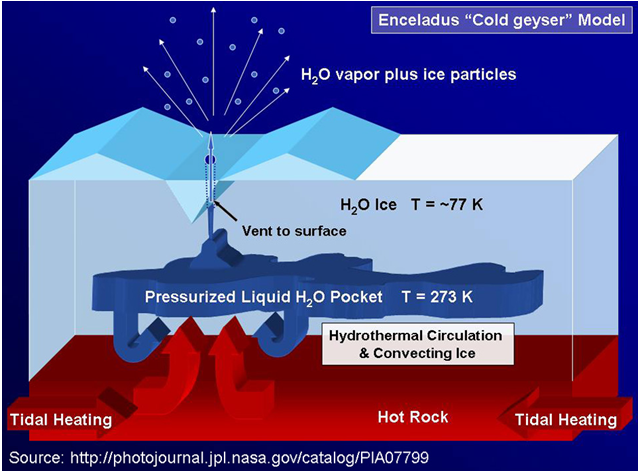 Eruption of water or other liquid or vapor-phase volatiles (collectively referred to as “cryomagma”), together with gas-driven solid fragments, onto the surface of a planetThe term "planet" originally comes from the Greek word for "wanderer" since these objects were seen to move in the sky independently from the background of fixed stars that moved together through the seasons. The IAU last defined the term planet in 2006, however the new definition has remained controversial. Click on Term to Read More or moon due to internal heating. After eruption cryomagmaWater or other liquid or vapor-phase volatiles together with gas-driven solid fragments produced by internal heating of a planetary body. Click on Term to Read More condenses to a solid form when exposed to the very low surrounding temperature. Cryovolcanism is not known to exist on Earth. Ice volcanoes were first observed on Neptune’s moon Triton during the Voyager 2 flyby. Indirect evidence of cryovolcanic activity has since been observed on several other icy moons of our solar systemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids., including Europa, Ganymede, and Enceladus. The Cassini-Huygens mission has found a methane-spewing cryovolcano on Titan, and such volcanism is now believed to be a significant source of the methane found in Titan’s atmosphere.
Eruption of water or other liquid or vapor-phase volatiles (collectively referred to as “cryomagma”), together with gas-driven solid fragments, onto the surface of a planetThe term "planet" originally comes from the Greek word for "wanderer" since these objects were seen to move in the sky independently from the background of fixed stars that moved together through the seasons. The IAU last defined the term planet in 2006, however the new definition has remained controversial. Click on Term to Read More or moon due to internal heating. After eruption cryomagmaWater or other liquid or vapor-phase volatiles together with gas-driven solid fragments produced by internal heating of a planetary body. Click on Term to Read More condenses to a solid form when exposed to the very low surrounding temperature. Cryovolcanism is not known to exist on Earth. Ice volcanoes were first observed on Neptune’s moon Triton during the Voyager 2 flyby. Indirect evidence of cryovolcanic activity has since been observed on several other icy moons of our solar systemThe Sun and set of objects orbiting around it including planets and their moons and rings, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids., including Europa, Ganymede, and Enceladus. The Cassini-Huygens mission has found a methane-spewing cryovolcano on Titan, and such volcanism is now believed to be a significant source of the methane found in Titan’s atmosphere.
Some or all content above used with permission from J. H. Wittke.






