Core
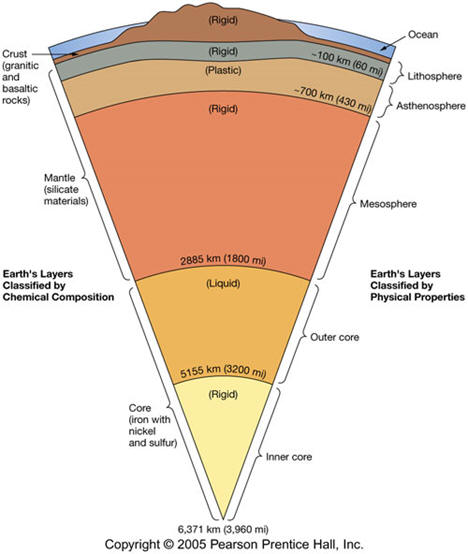
In the context of planetary formation, the core is the central region of a large differentiated asteroid, planetThe term "planet" originally comes from the Greek word for "wanderer" since these objects were seen to move in the sky independently from the background of fixed stars that moved together through the seasons. The IAU last defined the term planet in 2006, however the new definition has remained controversial. or moon and made up of denser materials than the surrounding mantleMain silicate-rich zone within a planet between the crust and metallic core. The mantle accounts for 82% of Earth's volume and is composed of silicate minerals rich in Mg. The temperature of the mantle can be as high as 3,700 °C. Heat generated in the core causes convection currents in and crustOutermost layer of a differentiated planet, asteroid or moon, usually consisting of silicate rock and extending no more than 10s of km from the surface. The term is also applied to icy bodies, in which case it is composed of ices, frozen gases, and accumulated meteoritic material. On Earth, the. For example, the cores of the Earth, the terrestrial planetsRocky planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These planets have physical characteristics, chemical composition and internal structure similar to the Earth. The terrestrial planets have 0.4% of the total mass of all the planets in the Solar System. Some large satellites of planets are also similar to the characteristics of and differentiated asteroids are rich in metallic iron-nickel.






